9F,Bldg.A Dongshengmingdu Plaza,No.21 Chaoyang East Road,Lianyungang Jiangsu,China +86-13951255589 [email protected]
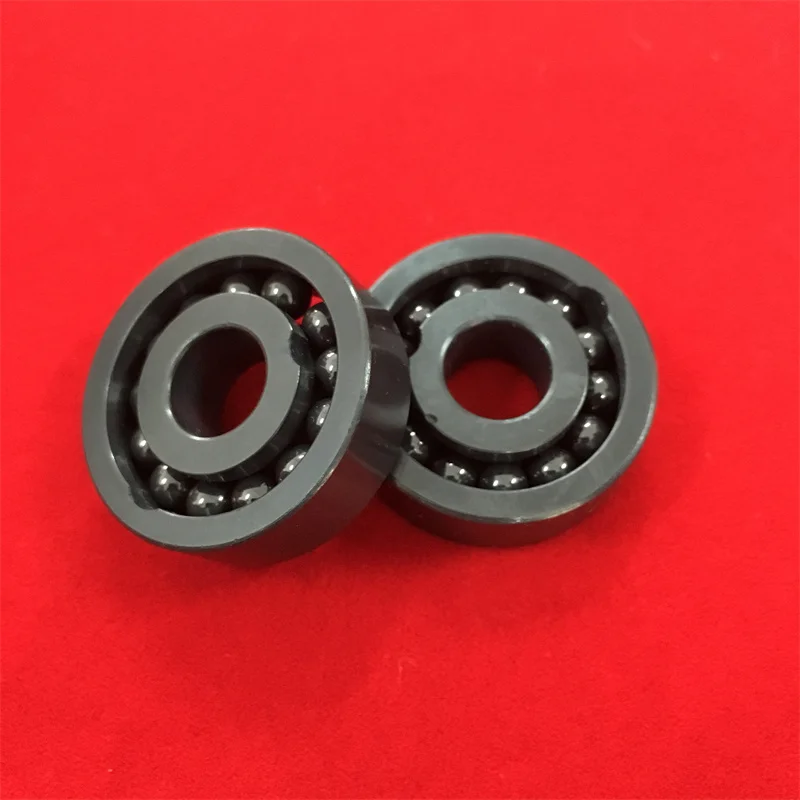

Silicon nitride ceramic bearings keep friction really low at around 0.05 to 0.15 coefficients even when pushed through intense heat and mechanical stress. These bearings beat steel ones by about 40 to 60 percent once they hit speeds over 20,000 RPM. The special bond between silicon and nitrogen atoms helps fight off wear caused by thermal expansion, so these bearings can keep running smoothly past 800 degrees Celsius without breaking down. Because of this stability, machines using them actually consume 12 to 18 percent less energy in precision spindle applications. What's more, there's no risk of micro welding happening when loads suddenly change. This happens because the material naturally lubricates itself and doesn't react much with other surfaces, making it ideal for demanding industrial environments where reliability matters most.
When machines spin faster than 250,000 RPM, something interesting happens to the oil films in regular metal bearings. The centrifugal force just smashes right through them, causing direct metal contact that wears everything down fast. This is where silicon nitride ceramics really shine because they have three main advantages working together. First, their surfaces actually attract lubricants about three times better than regular steel does. Second, these materials handle heat much better, keeping oils from breaking down even when temperatures climb past 120 degrees Celsius. And third, they're significantly stiffer than steel with an elastic modulus around 50% higher, so the bearing races don't get deformed under stress. All combined, these properties maintain an incredibly thin lubricant film, sometimes as small as 0.1 micrometers thick. For those running high-speed machining centers, this means spindles can run continuously for nearly 18,000 hours before needing maintenance. That's roughly three times longer than what traditional steel bearings would last under similar conditions.
Silicon nitride ceramic bearings offer exceptional wear resistance because they combine several key properties at once. These include impressive hardness levels above HV 1500, good fracture toughness around 6 to 7 MPa m squared root, plus outstanding ability to resist oxidation even when temperatures reach as high as 1000 degrees Celsius. The hardness helps prevent abrasion and surface damage while the fracture toughness stops cracks from spreading during repeated stress or sudden impacts. Oxidation resistance keeps surfaces intact in harsh conditions where both heat and chemicals are present. This combination makes them work really well in places like chemical processing equipment and industrial furnaces where traditional metal bearings simply cannot last very long before failing. Real world testing shows these ceramic bearings experience about 60 percent less wear than standard steel alternatives, which means longer time between maintenance checks and fewer unexpected shutdowns for manufacturing operations.
Si3N4 ceramic bearings might come with a bigger price tag upfront compared to traditional options, but they last three times longer in precision spindles and feed drive applications, which means real savings over time. What makes these ceramics stand out? They're super hard, resist cracking under stress, and handle heat much better than steel when spinning at those high RPMs we see in modern machinery. This combination basically stops the kind of wear and tear that typically takes down metal bearings months ahead of schedule. Maintenance teams report fewer breakdowns and less frequent replacements, something that adds up to significant cost reductions across production cycles.
Over a standard five-year equipment lifecycle, facilities realize a 55–70% reduction in total cost of ownership—making Si₃N₄ a strategic investment for operations prioritizing reliability, uptime, and lean maintenance budgets.
Ceramic bearings made from silicon nitride (Si3N4) have become essential in aerospace turbomachinery applications like jet engine auxiliaries and rocket fuel pumps. These bearings can handle speeds well over 250 thousand RPM in vacuum environments where traditional steel bearings fail due to cold welding issues. The fact that they're not metallic means there's no metal-to-metal sticking problems. Plus, these materials maintain their shape even when exposed to extreme heat above 1200 degrees Celsius, which keeps things running smoothly. Weighing in at about 40% less than steel counterparts, this reduced mass significantly cuts down on centrifugal forces acting on the components. This helps prevent component warping and maintains proper rotor behavior that's absolutely vital for successful missions in space or high altitude operations.
Silicon nitride (Si3N4) bearings in MRI and CT machines help cut down on image distortion caused by vibrations thanks to their consistent material properties and extremely smooth surfaces with less than 0.05 micrometer roughness. These bearings spin much smoother and quieter compared to traditional metal options. Another big plus? They're electrically insulating, so they stop those pesky eddy currents from messing up magnetic fields. Plus, this insulation keeps electric vehicle motors safe from electrolytic corrosion problems caused by stray currents. Components last about three times longer when using these bearings. Electromagnetic interference gets suppressed too, and there's noticeably less noise coming from high-end electric vehicle drivetrains. This means better diagnostic results for medical imaging while passengers enjoy a quieter ride, all without any loss in power output.