9F,Bldg.A Dongshengmingdu Plaza,No.21 Chaoyang East Road,Lianyungang Jiangsu,China +86-13951255589 [email protected]
High Power Resistors, have high power capacity, good wet & heat resistance, good resistance to electrical impulses and high voltage thick film resistor, welcome inquire HIGHBORN.
Resistor, abbreviated as resistor (resistor, usually denoted by "R"), is the most frequently used component in all electronic circuits. The main physical characteristic of a resistor is that it converts electrical energy into heat energy, meaning it is an energy-consuming component, and internal energy is generated when current passes through it. Its primary function is to obstruct the flow of current and is used for current limiting, voltage dividing, voltage dropping, load handling, cooperating with capacitors for filtering, and impedance matching. In digital circuits, its functions include pull-up and pull-down resistors.
Thick-film resistors mainly refer to resistors made using thick-film printing technology.
These resistors can be rectangular, strip-shaped, curvature-shaped, or other forms.
They are commonly used in the manufacture of precision resistors and power resistors.
Common thick-film resistors are made by printing and sintering a metal-ruthenium based resistor paste.
The resistor paste contains ruthenium oxide, organic solvents, and glass beads.
After sintering, the resistor consists of two components: the resistance of the ruthenium oxide itself and the barrier resistance.
Common type:
Type 1: Thick Film High Voltage Resistors and HIGH VALUE RESISTORS RADIAL LEADED
Lead spacing can be adjusted by bending
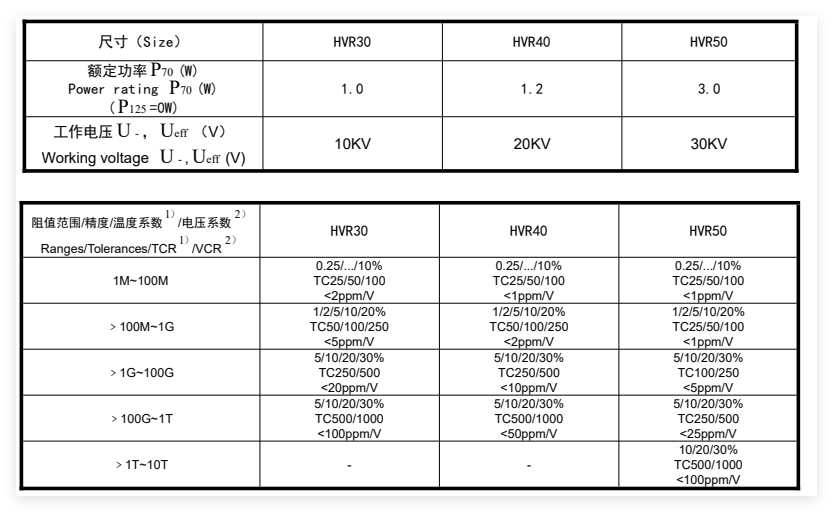
Resistance up to 10 TΩ
Low temperature coefficient, low voltage coefficient
Inductive-free design
High precision
Wide resistance range
High withstand voltage
High voltage resistors are mainly used for various types of shunting, voltage discharge, voltage division, high-voltage power transmission and transformation, with detection and calculation conducted using high voltage resistors. They are used in voltage dividers, discharge resistors, and are commonly found in various electronic circuits including PCB thick film circuits.
Type 2: Power Thick Film Resistors
35 series, 35A series
50 series
100 series
200 series
35W TO-220 package (through-hole resistor)
35W TO-263 package (bent angle SMD resistor)
50W TO-220 package
100W TO-247 package
200W TO-227 package
Applications: Used in high-power electrical appliances/circuits (in this case, SMD resistors cannot be used, as the maximum power for SMD is 2-3W).
Type 3: HIGH–MEGOHM CHIP RESISTORS
This product is essentially an insulator with high resistance.
Its use is similar to HVR high-voltage resistors, only the appearance is different.
Chip high-resistance resistors are soldered onto the circuit board.
Thick-film high-resistance chip resistor
Low temperature and low voltage operation
End PtAg electrodes for bonding and soldering
Non-grooved type is used for higher voltage applications, up to 6000V
Features of resistors:
High voltage resistors in thick film
Variable lead spacing by bending n
Resistance values up to 10 Teraohm
Low values of TCR and VCR
Excellent solderability
Perfect resistance tolerance
Custom product with the quantity they prefer is also available
Order data:
Type——value——tolerance——TCR——measuring voltage
GST4020 10G ±10% TCR100 20V
If no data for TCR and measuring voltage are supplied,the standard value and measuring voltage of 10V is used.
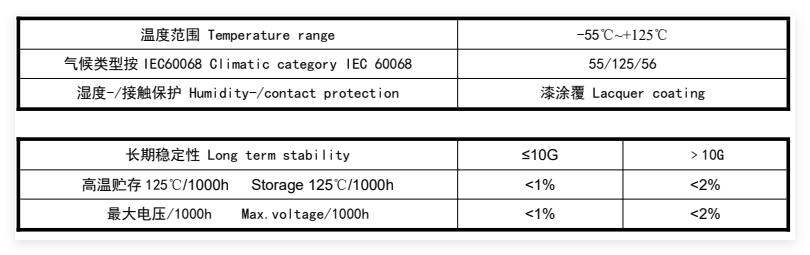
Resistors in circuits usually play the role of voltage division and current splitting. Both AC and DC signals can pass through resistors. When working in high-temperature environments, it is necessary to select resistors that can withstand higher temperatures and remain stable, such as metal oxide resistors. Accuracy and tolerance refer to the range of deviation in resistor values. In some high-precision applications, resistors with smaller tolerances need to be selected. Common tolerance levels are 1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, etc.
High-precision Resistors
In some circuits that require strict control of current or voltage, high-precision resistors must be selected, such as metal film resistors. Higher-precision resistors can ensure that the circuit operates stably under set conditions, avoiding performance fluctuations caused by errors.
Tolerance and Application
Generally speaking, precision instruments and measuring devices require smaller tolerances, while for ordinary power supply circuits or signal processing circuits, resistors with larger tolerances are sufficient.
Temperature Coefficient and Stability
The temperature coefficient (TC) is the proportion by which a resistor changes with temperature, usually expressed in ppm/°C. For applications with significant temperature fluctuations, it is very important to choose resistors with a lower temperature coefficient to ensure the stability of the resistor value under different operating temperatures.
All resistors have a certain resistance value, which represents the degree to which the resistor opposes the flow of electric current.
The unit of resistance is the ohm, represented by the symbol 'Ω'.
An ohm is defined as follows: if a voltage of 1 volt is applied across a resistor and a current of 1 ampere flows through it, the resistance of the resistor is 1 ohm.
In the International System of Units, the unit of resistance is Ω (ohm), and there are also KΩ (kilo-ohm) and MΩ (mega-ohm), where: 1 MΩ = 1000 KΩ, 1 KΩ = 1000 Ω.
The electrical performance indicators of resistors typically include nominal resistance, tolerance, and rated power.
Resistors, together with other components, form functional circuits, such as RC circuits.
Technical Specifications


Aluminum Nitride Rod High Thermal Conductivity for Electronics & Semiconductor Cooling
Wear Resistant Al2o3 Alumina Ceramic Plate for Protecting Tube

Alumina Ceramic Rings High-Precision Filtration & Chemical Resistance for Water Treatment
Alumina Ceramic Insulator Precise Dimensional Accuracy for Electronic Components