9F,Bldg.A Dongshengmingdu Plaza,No.21 Chaoyang East Road,Lianyungang Jiangsu,China +86-13951255589 [email protected]
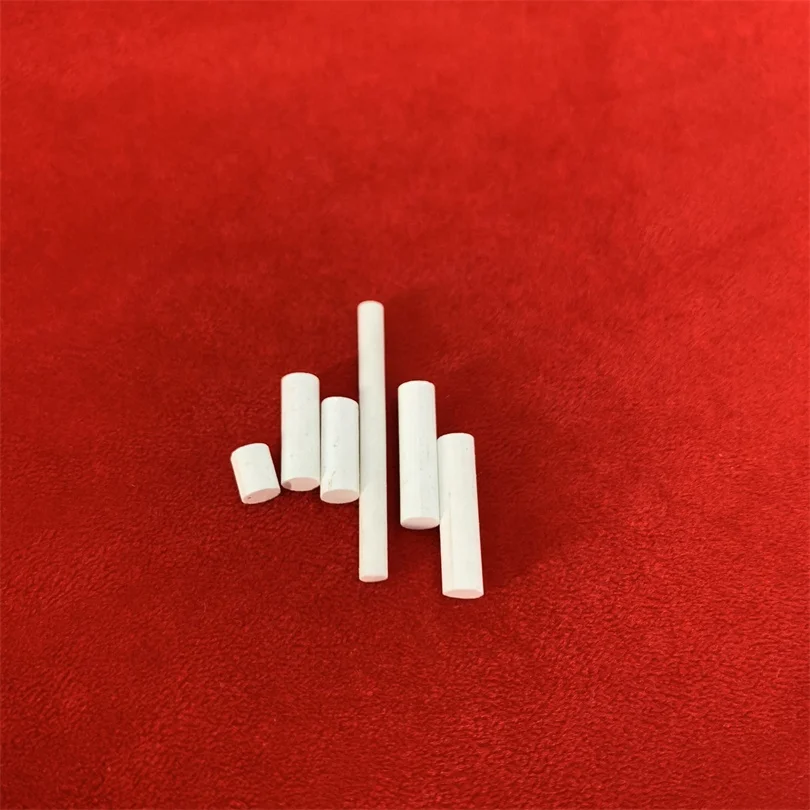
Porous Ceramics High Permeability Reference Electrode Core
The high-permeability reference electrode wick, a precision component made of porous ceramics, plays a crucial role in electrochemical systems. It enables controlled and precise ion transport, ensuring the stable potential of reference electrodes. This makes it a key element for accurate electrochemical measurements, widely used in various analytical and industrial applications where potential stability and measurement accuracy are paramount.
Detailed Description
Porous ceramics hold an irreplaceable position in numerous industrial and scientific fields, and the high-permeability reference electrode (electrode wick) stands out as one of the core components in electrochemical systems. Classified as "Electrode Wick" in the porous ceramic property table, this component features a series of exclusive characteristics that enable it to play a key role in reference electrodes, with remarkable performance particularly in the dimension of high permeability.
In terms of physical structure and performance parameters, the electrode wick has a density range of 1.8–2.2 g/cm³. Compared with plant water-absorbing wicks, ceramic core rods, and similar materials (with a density of 0.8–1.2 g/cm³), this density makes it a relatively dense porous ceramic product. The high density endows it with excellent mechanical stability, allowing it to maintain structural integrity in the complex environment of electrochemical cells and avoid deformation or damage.
Porosity is the core factor determining its high permeability performance. The electrode wick has an open porosity of 20–30% and a total porosity of 25–40%. Open porosity refers to the proportion of pore volume that is interconnected and exposed to the surface, while total porosity includes the sum of open pores and closed pores. Although its open porosity value is not particularly prominent when compared with materials such as plant water-absorbing wicks (with an open porosity of 50–60%), the "high permeability" here focuses on the controllability and precision of ion transport rather than the mere size of pore volume. Its pore structure, with a pore size of 1–3 μm, is specifically designed to achieve selective and efficient ion migration. This refined pore architecture ensures that ions can pass through the material at a rate that maintains the stable potential of the reference electrode, which is the fundamental prerequisite for accurate electrochemical measurements.
The water absorption rate of the electrode wick is 10–28%. This range means it can absorb an appropriate amount of electrolyte, which is crucial for sustaining the continuous progress of electrochemical reactions and maintaining long-term stable potential. Unlike materials designed for extreme water absorption, the water absorption rate of the electrode wick is optimized to achieve permeability balance—it not only ensures sufficient electrolyte penetration to support ion exchange but also prevents electrolyte leakage or abnormal potential fluctuations caused by excessive penetration.
In the application scenario of reference electrodes, the electrode wick serves as the key interface between the internal electrolyte of the reference electrode and the external test solution. Its porous structure, characterized by controlled high permeability, can realize the controlled migration of ions (such as potassium ions in saturated calomel electrodes, silver ions in silver/silver chloride electrodes, etc.). This controlled ion migration is essential for the reference electrode's potential to remain stable and reproducible. The moderate open porosity, specific pore size specifications, and controlled water absorption work together to ensure this stability. The "high permeability" here is an engineered permeability—it does not pursue the maximization of pore space but creates a material that can precisely regulate ion flow, which is the core essence of a reliable reference electrode.
Deviations in these performance parameters will directly lead to fluctuations in electrode potential, thereby undermining the accuracy of electrochemical measurements. For example, excessively high porosity will cause the electrode to lose electrolyte too quickly, resulting in potential drift; excessively low porosity will hinder ion transport, leading to slow response or distorted readings.
In summary, the high-permeability reference electrode (electrode wick) made of porous ceramic is a precision component with carefully calibrated performance parameters. The synergistic effect of its density, porosity, water absorption rate, pore size, and other properties enables it to assume a key role in electrochemical systems. Its design fully reflects the decisive role of the precision of material properties in the reliability and accuracy of reference electrodes in various analytical and industrial applications. The "high permeability" here is the result of sophisticated engineering design; it is not only a performance value but also an exclusive characteristic customized to meet the stringent requirements of electrochemical potential stability.
In the field of electrochemical analysis, the stability of reference electrodes serves as the cornerstone for ensuring measurement accuracy, with high-permeability reference electrode sand cores playing an irreplaceable role. In industrial electrochemical monitoring, such as potentiometric titration for water quality analysis and electrode potential calibration in battery research, these sand cores maintain ion transport stability under complex temperature and electrolyte concentration variations, keeping reference electrode potential fluctuations within an extremely narrow range to meet high-precision analytical requirements.
From the perspective of material research and development, traditional reference electrode assemblies exhibit shortcomings in ion transport controllability—either ion migration is too rapid, leading to severe electrolyte consumption, or too slow, affecting response speed. The high-permeability reference electrode sand core achieves "controlled permeability" in ion transport through precise regulation of parameters such as density, porosity, and pore size in porous ceramics. This design concept also provides valuable insights for the development of other electrochemical functional ceramic components.
Moreover, in terms of service life, due to its excellent mechanical stability, this sand core can maintain structural integrity during prolonged electrochemical cycling and frequent electrode maintenance operations, effectively reducing the replacement frequency of reference electrodes. This significantly enhances operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in industrial continuous monitoring scenarios.


Product Parameters Table
| Item | Infiltration Cup | Plant Water Absorbing Wick | Electrode Wick | Ceramic Wick | Scented Ceramic | |
| White alumina | Silicon Carbide | |||||
| Density(g/cm³) | 1.6-2.0 | 0.8-1.2 | 1.8-2.2 | 0.8-1.2 | 1.6-2.0 | 1.7-2.0 |
| Open Porosity Rate(%) | 30-40 | 50-60 | 20-30 | 40-60 | 30-45 | 35-40 |
| Porosity Rate(%) | 40-50 | 60-75 | 25-40 | 60-75 | 40-50 | 40-45 |
| Water Absorption(%) | 25-40 | 40-70 | 10-28 | 40-70 | 25-40 | 25-35 |
| Pore Size(μm) | 1-5 | 1-3 | 1-3 | 1-3 | 1-5 | 1-10 |