Brief
1. Advantages of Quartz Cuvette cell:
- ·Quartz Cuvette with high Accuracy and Precision: Enable highly accurate and reproducible optical measurements.
- · Quartz Cell Path Length Consistency: Provide a fixed, reproducible path length, which is critical for quantitative analysis.
- · Quartz cell Versatility: Compatible with a wide range of samples (liquids, gases) and solvents.
- · Quartz cuvette Optical Clarity: Made from materials (e.g., quartz, glass) that offer excellent transmission at specific wavelengths.
- · Quartz cell Durability and Reusability: High-quality cuvettes (e.g., quartz, glass) are durable and can be cleaned and reused multiple times.
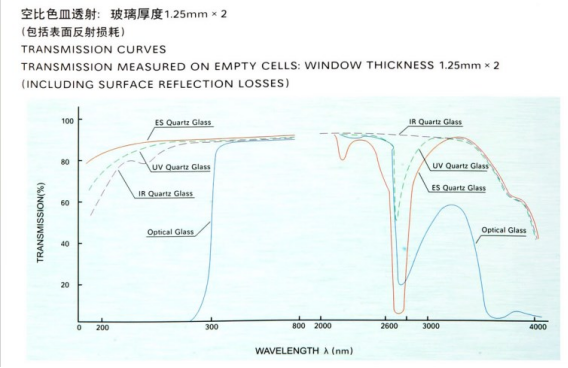
According to the wavelength range used, cuvettes can be classified into visible light series (glass cuvettes), ultraviolet-visible light series (quartz cuvettes), and infrared light series (infrared quartz cuvettes). In ultraviolet photometric experiments, glass cuvettes and quartz cuvettes are usually selected. It is worth noting that in the ultraviolet region, since glass cuvettes strongly absorb ultraviolet light, which can affect the experimental data and results, quartz cuvettes that do not absorb ultraviolet light are usually selected. In the visible light region, the influence of glass cuvettes is relatively small and can be ignored. Both glass cuvettes and quartz cuvettes can be used. However, considering economic factors, since the price of glass cuvettes is much lower than that of quartz cuvettes, glass cuvettes are more often chosen for use in the visible light region.
2.Application of quartz cuvette cell:
Quartz cuvette cell is used in chemical industry, metallurgy, medical, pharmaceutical, food, environmental protection, power plants, water plants, oil and other industries, departments and colleges and universities, and laboratory etc.
3.Instructions for Quartz cuvette cell Use:
-
1). Orientation and Placement in Spectrophotometer
- · Maintain Consistent Orientation: Always place the cuvette into the holder in the same orientation. Due to minor imperfections in glassware, readings can vary slightly depending on which face is in the light path. Marking the cuvette on one frosted side can help maintain consistency.
- · Ensure Proper Seating: Ensure the cuvette is seated squarely and securely in the designated compartment, so the light beam passes perfectly through the center of the two clear optical windows.
-
2). Chemical Compatibility
- · Know Your Cuvette Material: Different cuvette materials (e.g., glass, quartz, plastic) have different chemical resistances.
- · Glass: Suitable for visible wavelength range but can be etched by strong bases.
- · Quartz (Fused Silica): Essential for UV spectroscopy. Resistant to most acids and high temperatures.
- · Plastic (e.g., PS, PMMA): Disposable and inexpensive, but incompatible with many organic solvents (e.g., acetone, acetonitrile), which can dissolve or craze the plastic.
- · Never Use Abrasive Cleaners: Do not use abrasive brushes or cleaners, as they will permanently scratch the optical surfaces.
Management and maintenance of cell cuvettes
- (1) Select the appropriate cuvette material according to the wavelength required for the experiment. In the ultraviolet region, quartz cuvettes should be selected, while in the visible region, both glass and quartz cuvettes can be used. Considering economy, glass cuvettes are usually selected for the visible light region. It is recommended to implement a system of dedicated personnel or dedicated groups for dedicated use. After use, the cuvettes should be cleaned up and returned in a timely manner to avoid confusion and ensure the accuracy of cuvette matching.
- (2) Try to ensure that each ultraviolet spectrophotometer is equipped with a dedicated matching cuvette to avoid cross-use. If cross-use is required, records should be made and the original state should be restored in a timely manner after use.
- (3)The used cuvettes should be cleaned immediately and dried naturally in a well-ventilated and cool place. After drying, put it in the corresponding storage container. When placing, ensure that the storage container is clean and dry, and follow the principle of "smooth side up, rough side on both sides". This makes it easier to access and prevents the smooth side from being contaminated.
Identification of cuvettes
Through vision and hearing, we can observe and compare the appearance and clarity of the cuvette to make a distinction.
The specific methods include:
- (1) Observe the letter markings on the cuvette.
The rim of a Glass cuvette is usually marked with "G" (Glass), while a Quartz cuvette is marked with "Q" (Quartz) or "QS/S" (Quartz glass).
- (2) If there is no letter marking or the marking is worn out, it can be judged by observing the edge surface at the rim. The fracture surface of ordinary glass is light green, that of boric acid glass is whitish, while the cross-section of quartz is transparent. Therefore, when looking down from the rim, if the edge appears green, it is made of glass.
If it is transparent or white, it may be made of quartz.
- (3) Tapping the cuvette can also help identify its material.
When a quartz cuvette is struck, it makes a clear sound, while a glass cuvette makes a muffled sound.
- (4) The hardness of quartz is higher than that of glass. Therefore, when grinding, the wear of quartz cuvettes is much smaller, while that of glass cuvettes is greater.
- (5) When using an incandescent lamp to illuminate a cuvette, the glass cuvette has a higher light transmittance, while the quartz cuvette should appear slightly cloudy.
Technical parameters of Cuvette:
Material |
Code |
Transmission on empty cell |
Deviations in Matching |
Optical glass |
G |
at 350nm approx. 82% |
at 350nm max. 0.5% |
ES quartz glass |
Q |
at 200nm approx. 80% |
at 200nm max. 0.5% |
IR quartz glass |
I |
at 2730nm approx. 88% |
at 2730nm max. 0.5% |