9F,Bldg.A Dongshengmingdu Plaza,No.21 Chaoyang East Road,Lianyungang Jiangsu,China +86-13951255589 [email protected]
Soil Tensiometer Sensor Water Absorbing Ergometer. Buy now! Limited-time discount!
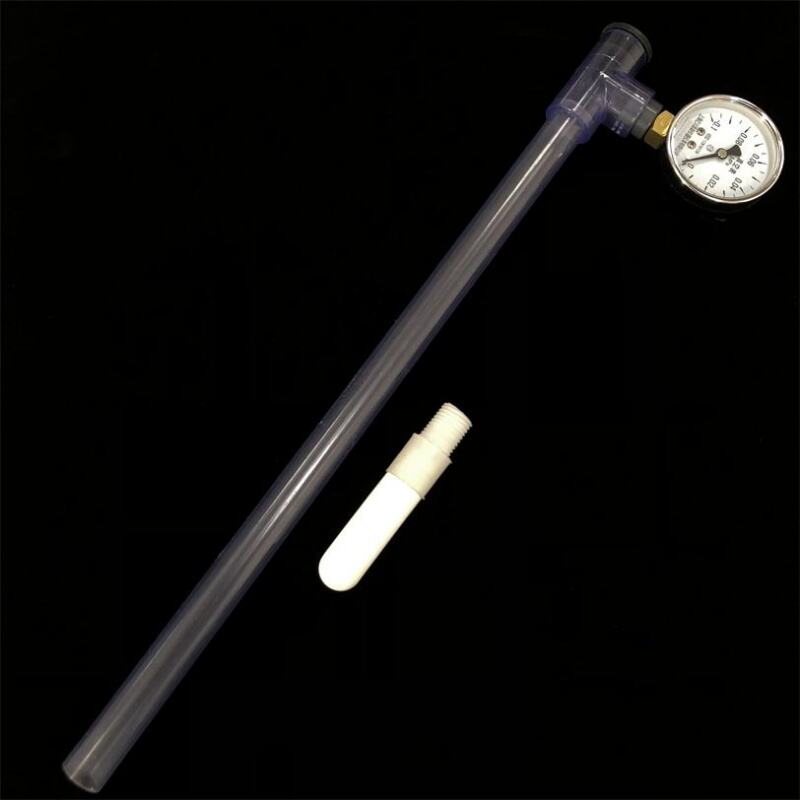
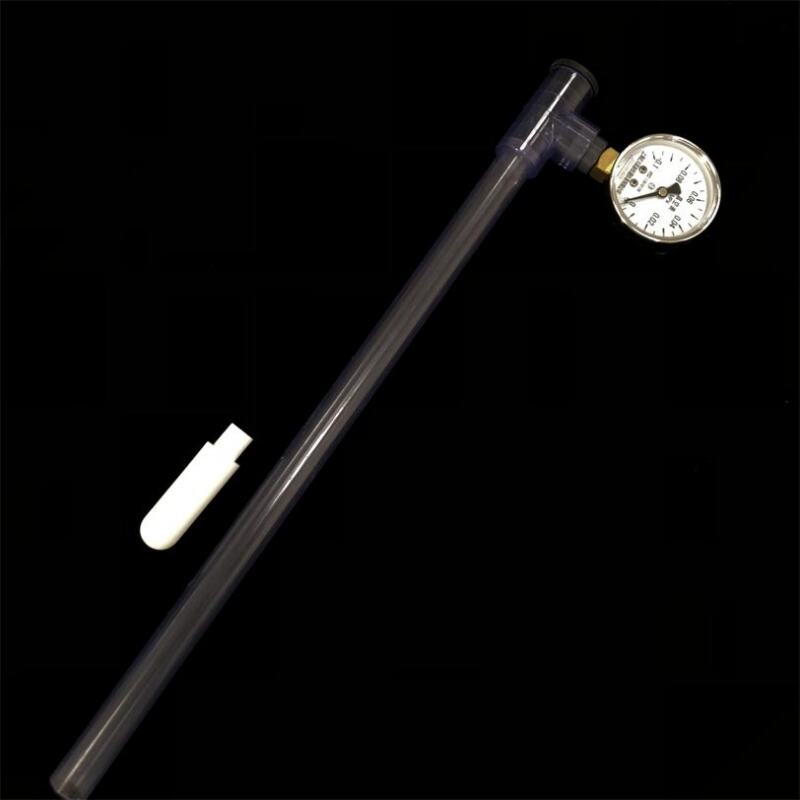
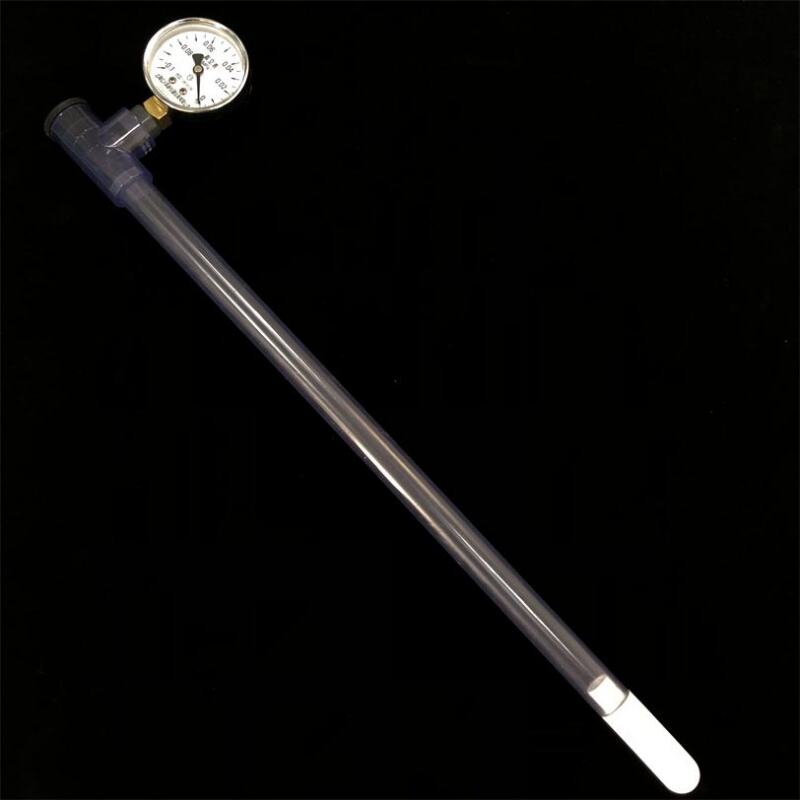
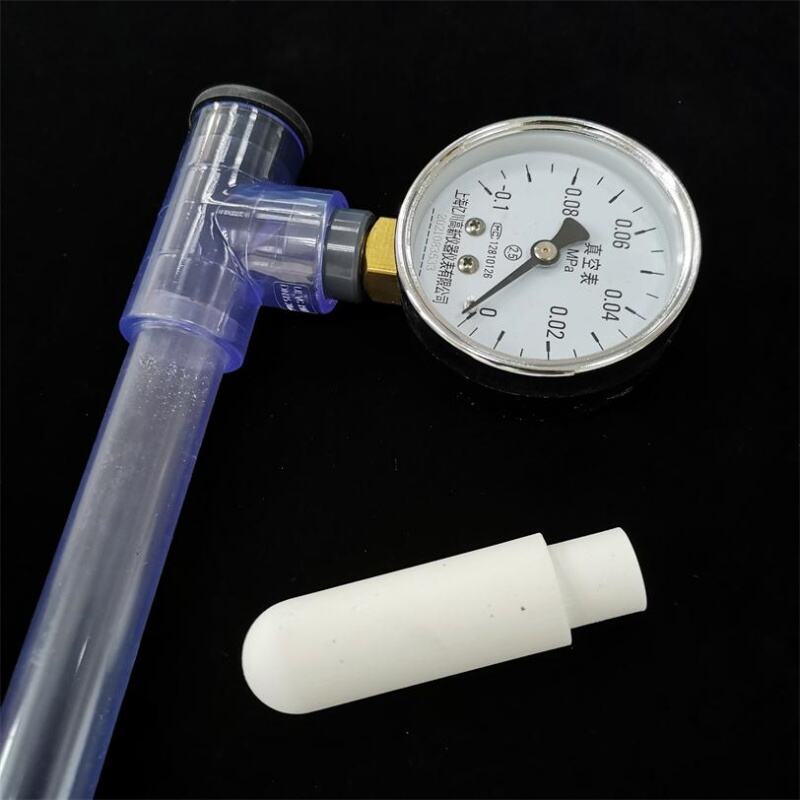
A complete set of soil tensiometers consists of porous ceramic tubes, UPVC tubes, tee-junction, threaded plugs, vacuum gauge connectors and vacuum gauges. Soil moisture tensiometer is an instrument that measures soil moisture by using negative pressure. Measuring soil moisture content can effectively understand the soil condition. It provides a scientific basis for guiding agricultural irrigation and achieving precise agricultural production.
The soil water tension measured by a tensiometer is the suction force of the soil for water. The wetter the soil is, the less it can absorb water. Conversely, it is large. When the soil moisture increases to the point where all voids are filled with water, the soil water tension will drop to zero. In other words, at this point, the soil moisture content has reached saturation. The saturated moisture content of various soils varies in terms of weight moisture content and volumetric moisture content, but they are all consistent with zero in terms of soil water tension.
Operating method of tensiometer
1. Boiling water for cooling: Boil tap water for 20 minutes and then let it cool down for later use.
2. Water filling: Open the cover of the water collection pipe and tilt the instrument. Slowly fill the plastic bottle with boiled and cooled water until it is full. Stand the instrument upright for 10 to 20 minutes (without covering the cover), allowing the water to moisten the ceramic tube and water to drip from the surface of the ceramic tube.
3. Venting: Fill the instrument with water again. Use a dry cloth or paper with good water absorption to draw water from the surface of the ceramic tube (or insert a rubber stopper with an injection needle into the water injection point and use a syringe to evacuate air. When evacuating, make sure the needle tip passes through the rubber stopper and extends into the interior of the instrument.) At the same time, press the rubber stopper with your left hand to prevent it from loosening and leaking air. At this point, bubbles can be seen overflowing from the vacuum gauge and gradually gathering in the gas collection pipe. Slowly pull out the stopper to allow the pointer of the vacuum gauge to slowly return to zero. Continue to fill the instrument with anhydrous water and still perform the vacuuming using the above method. Repeat this process 3 to 4 times, and most of the air inside the vacuum gauge can be removed.
4. Gas collection: Fill the instrument with anhydrous water, add a stopper, seal it, and stand the instrument upright to allow the ceramic tube to evaporate in the air. At this point, buried bubbles will overflow from the ceramic tube vacuum gauge, plastic tube and gas collection pipe. Meanwhile, gently invert the instrument up and down to concentrate the bubbles in the gas collection pipe.
5. Re-evaporation: Immerse the ceramic tube in water. At this point, you can see the vacuum gauge pointer return to zero. Open the lid, refill it with water, put the lid back on, and let the ceramic tube evaporate in the air again. At the same time, gently invert the instrument up and down to collect the overflowing air.
6. Repeat: Follow the above steps 2 to 3 times. After each repetition, the pointer of the vacuum gauge can rise higher until the ceramic tube is immersed in water and the vacuum pointer returns to zero. Open the lid, fill it with water, close the lid tightly, and immerse the clay tube in the anhydrous water for later use.
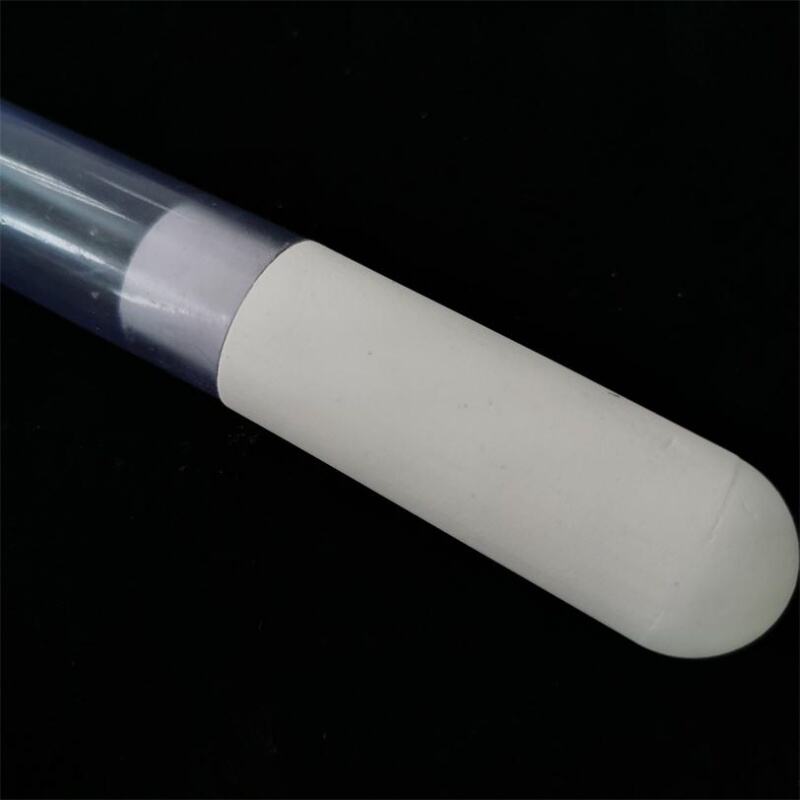


Porous Ceramics
| Item | Infiltration Cup | Plant Water Absorbing Wick | Electrode Wick | Ceramic Wick | Scented Ceramic | |
| White alumina | Silicon Carbide | |||||
| Density(g/cm³) | 1.6-2.0 | 0.8-1.2 | 1.8-2.2 | 0.8-1.2 | 1.6-2.0 | 1.7-2.0 |
| Open Porosity Rate(%) | 30-40 | 50-60 | 20-30 | 40-60 | 30-45 | 35-40 |
| Porosity Rate(%) | 40-50 | 60-75 | 25-40 | 60-75 | 40-50 | 40-45 |
| Water Absorption(%) | 25-40 | 40-70 | 10-28 | 40-70 | 25-40 | 25-35 |
| Pore Size(μm) | 1-5 | 1-3 | 1-3 | 1-3 | 1-5 | 1-10 |
Precautions