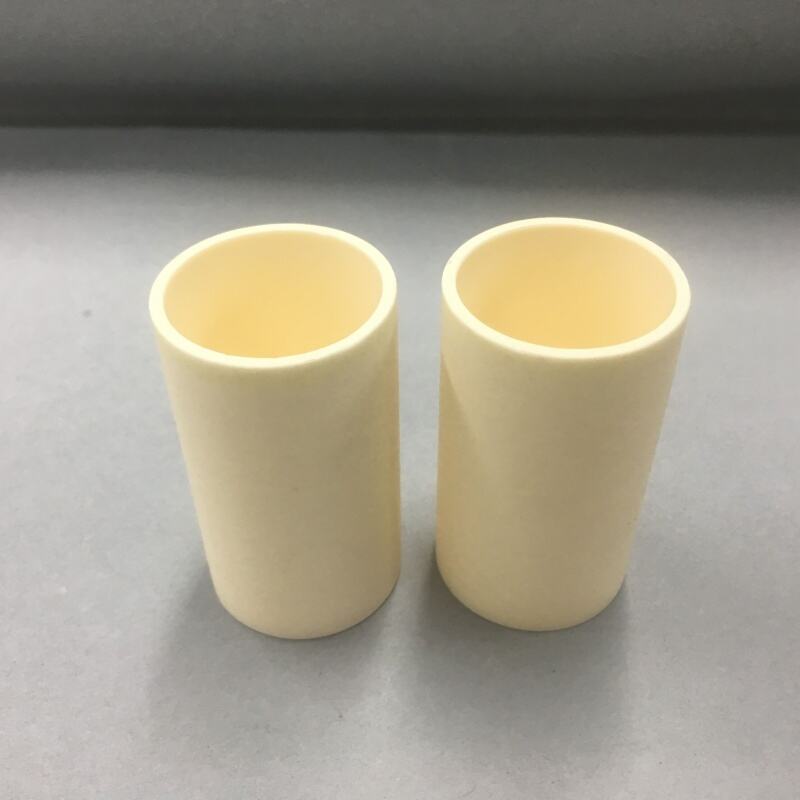
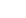
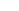
Alumina ceramic crucibles, also known as corundum ceramic crucibles, are containers with strong high-temperature resistance. They can withstand temperatures as high as 1650℃ and can also be used for a short period at 1800℃, making them suitable for high-temperature experiments and smelting processes. Alumina ceramics have excellent resistance to acids, alkalis and molten metals, which can effectively prevent sample contamination and ensure the accuracy of experimental results. In addition, the purity of alumina crucibles is usually above 99%, ensuring stability and reliability in high-temperature environments.
Alumina ceramic crucibles are available in various specifications and shapes, with capacities ranging from 5ml to 2500ml. Common shapes mainly include cylindrical, conical, arc-shaped, square, etc. According to different experimental requirements, different sizes and shapes can be customized to fit various equipment.
Alumina ceramic crucibles have a wide range of applications. They can be used for the analysis of various metal and non-metal samples and for melting materials in laboratories. They can also be used in shuttle kilns, pusher kilns to burn colorants, colorants, melts, pigments, luminescent materials, etc., as well as in small experimental kilns and experimental electric furnaces for preparation. Melting metals, precious metals, optical glass, used for the analysis and firing of mineral raw materials such as rare earths, and the firing of high-temperature products such as ceramic powders. Alumina crucibles represent a deeper development and exploration of crucible technology. They are now being used in an increasing number of practical applications and will bring more convenience to our lives in the future.
Alumina crucibles also include thermal analysis crucibles, which are mainly used for laboratory analysis and TGA instruments. The thermal analysis crucible has a high thermal conductivity, and the heat transfer speed between the sample and the crucible is fast to ensure that there is a very small temperature difference between the two. The structure and performance of the alumina ceramic crucible are stable. The high-purity powder, combined with the precisely controlled high-temperature sintering process, forms a dense and uniform microscopic crystal phase structure, ensuring that it is less likely to undergo physical and chemical reactions with the analyzed samples during use.
When cleaning alumina crucibles, the first thing we should pay attention to is that we must not use strong acids, strong alkalis or hard tools to clean the crucibles to avoid causing damage to them. Under normal circumstances, we can use mild detergent or alcohol to clean the surface of the crucible. For residues that are difficult to remove, you can try gently scrubbing with a soft brush, but be careful not to apply excessive force to avoid scratching the inner wall of the crucible.
In addition to daily cleaning, the maintenance of alumina crucibles is equally important. During use, sudden temperature changes should be avoided to prevent the crucible from cracking. When the crucible is taken out of the high-temperature environment, it should be placed on a dry and heat-insulating pad to cool down naturally. In addition, it is necessary to avoid exposing the crucible to a damp environment to prevent it from getting damp and affecting its usage effect.
When storing alumina crucibles, we should place them in a dry and well-ventilated area and avoid direct sunlight. At the same time, crucibles should be kept at a certain distance from each other to prevent damage caused by mutual collision. For crucibles that have not been used for a long time, regular cleaning and inspection should be carried out to ensure they are in good condition.
The following points should be noted when using alumina crucibles:
- 1.During handling, handle with care to avoid damage caused by dropping or shaking.
- 2. When storing, choose a dry and well-ventilated place or wooden rack to prevent performance from being affected by moisture.
- 3. Before use, it needs to be preheated to 500℃ through baking or other methods to ensure its stability and durability.
- 4. When adding materials, pay attention to the volume control to avoid excessive amount causing expansion and damage.
- 5. When in use, do not fill the molten material too full to prevent heated objects from jumping out and air from entering and exiting.
- 6.When choosing the appropriate tapping tools and crucibles, the middle part should be clamped to avoid local damage due to force.
Product Parameter Table
| Item |
Test Condition |
Unit Symbol |
95% |
99% |
85% |
| The main chemical ingredient |
|
|
Al₂O₃ |
Al₂O₃ |
Al₂O₃ |
| Bulk Density |
|
g/cm³ |
3.6 |
3.89 |
3.4 |
| Maximum Use Temperature |
|
|
1450°C |
1600°C |
1400°C |
| Water absorption |
|
% |
0 |
0 |
< 0.2 |
| Flexural strength |
20°C |
MPa (psi x 10³) |
358 (52) |
550 |
300 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion |
25 - 1000°C |
1×10⁻⁶/°C |
7.6 |
7.9 |
7 |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity |
20°C |
W/m·K |
16 |
30 |
|