9F,Bldg.A Dongshengmingdu Plaza,No.21 Chaoyang East Road,Lianyungang Jiangsu,China +86-13951255589 [email protected]
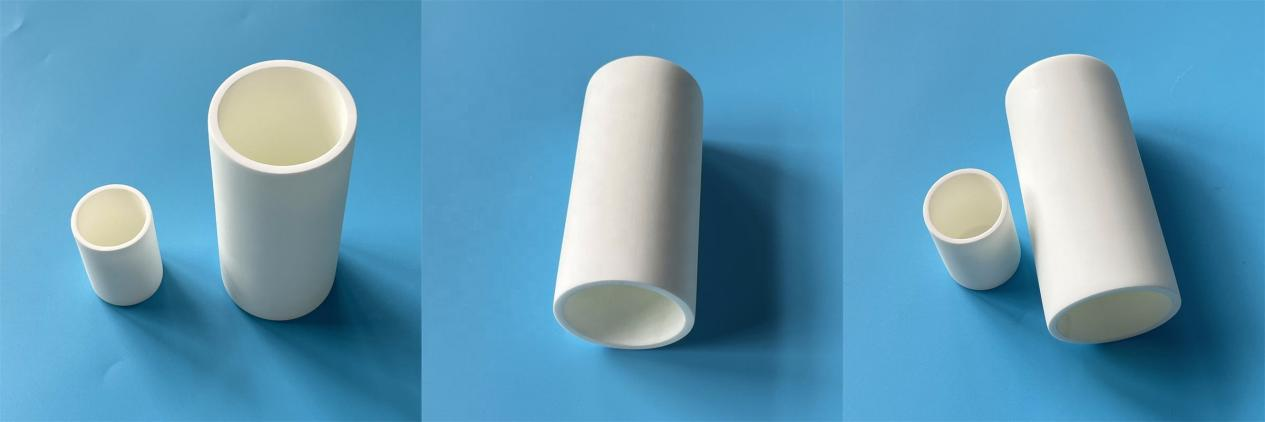
Magnesium oxide crucible is a high-performance laboratory high-temperature resistant container, mainly used for melting precious metals such as alloys, rare earths, platinum, rhodium, etc.
Magnesium oxide is an alkaline oxide with a high melting point, offering excellent chemical stability and heat resistance, making it suitable for processes involving molten metals, glass, ceramics, and other high-temperature treatments. Magnesium oxide crucibles are high-temperature resistant containers used for high-temperature experiments and industrial applications, primarily made from magnesium oxide (MgO). These crucibles are commonly employed in laboratories, metallurgy, chemical engineering, and materials science, particularly in scenarios requiring resistance to alkaline environments or high-temperature corrosion.
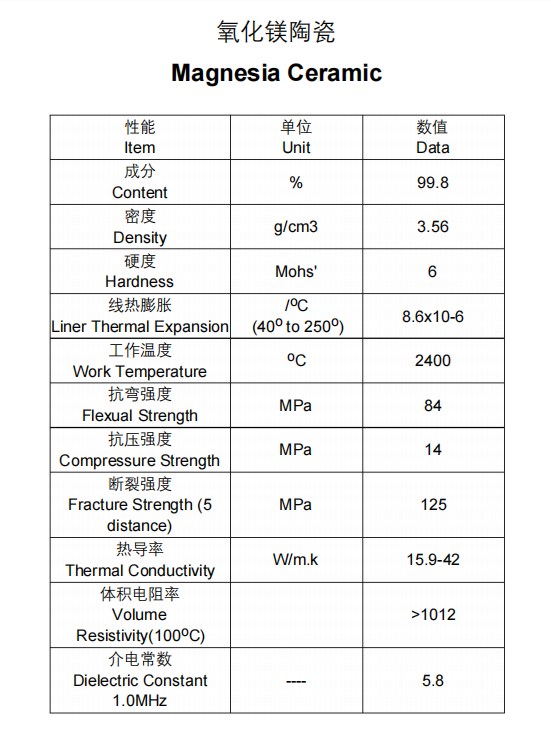
It is made of high-purity magnesium oxide (usually with a purity of over 99%) and has excellent high temperature resistance (maximum operating temperature of 2200 °C), wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and acid and alkali resistance. Magnesium oxide ceramics belong to the cubic crystal system, with a theoretical density of 2.8-3.2 g/cm ³ and a Mohs hardness of 5-6. They have a high specific volume resistance at high temperatures and good electrical insulation properties.
It is suitable for heating containers in medium and high frequency induction furnaces, electric furnaces, and vacuum furnaces, and can provide an inert and pollution-free environment to ensure high purity during the melting process.
In addition to the above characteristics, magnesium oxide crucibles also have good resistance to alkaline metal slag and can be used for smelting non-ferrous and precious metals such as platinum, rhodium, iridium, as well as vacuum melting high-purity radioactive metals such as uranium, thorium alloys, iron and their alloys.
In addition, it can also be used as a high-temperature thermocouple protection tube and a lining material for high-temperature furnaces.
Key Properties and Characteristics
Common Applications
MgO crucibles are used in demanding, high-temperature processes where other ceramics fail:
Melting and processing of reactive metals (e.g., Titanium, Zirconium, and their alloys).
Processing platinum group metals (Platinum, Rhodium, etc.).
Melting uraniumand other nuclear materials.
Crucibles for the Czochralski process to grow single crystals of
high-melting-point oxides.
Used in labs for sintering, calcination, and heat treatment of advanced
ceramics and powders where contamination must be avoided.
Occasionally used for containing certain types of specialty glasses,
particularly those with a basic composition.
Operation steps (taking metal melting as an example):
Preheating: Heat the crucible at a rate of 5-10 ° C/min to 500 ° C and hold for 1 hour.
Loading: Add metal material, with a filling amount not exceeding 80% of the crucible capacity.
Melting: Heat up at a rate of 10-15 ° C/min to the target temperature (usually 1200-1600 °C).
Insulation: Keep at the target temperature for 1-2 hours.
Cooling: Slowly cool to room temperature at a rate not exceeding 5 ° C/min. There are related products in the store now. Our zirconia ceramic crucible has a high purity of 99.9%, a Vickers hardness of 1250HV, and a density of 6.0g/cm ³. It can withstand high temperatures up to 1000 ° C and is suitable for various industrial fixed uses.

Important Handling and Usage Considerations
Technical Specifications

Heat Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Lab Melting

Non Inductive Thick Film High Frequency Resistor High Power Cylindrical High Voltage Resistor
High Temperature Heat Resistance Fused Quartz Glass Tube

Chemistry Laboratory Equipment 30mm 100mm 200mm Grey Natural Agate Mortar and Pestle Set