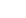
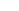
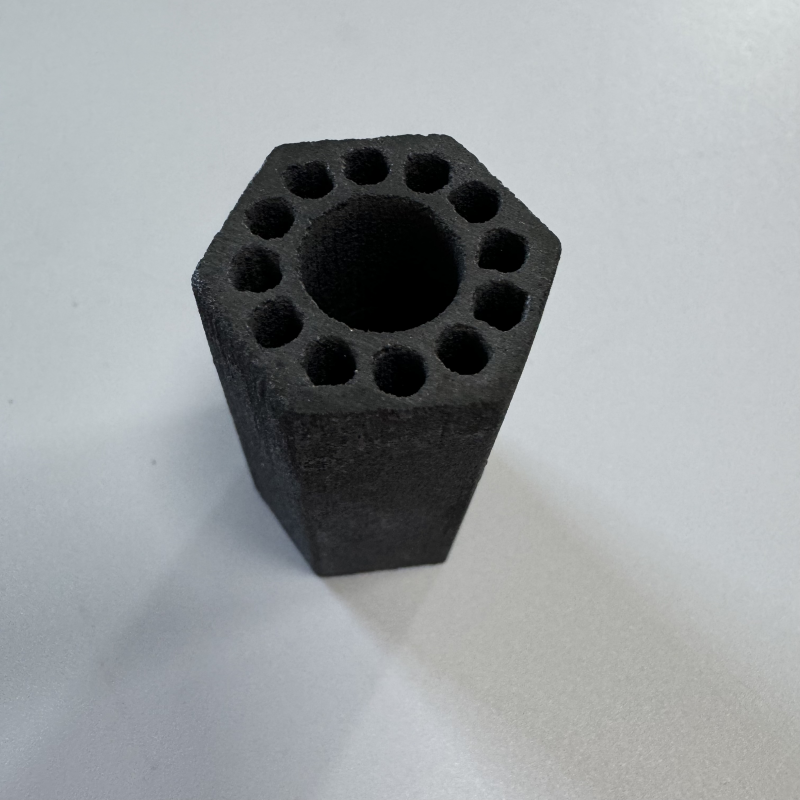
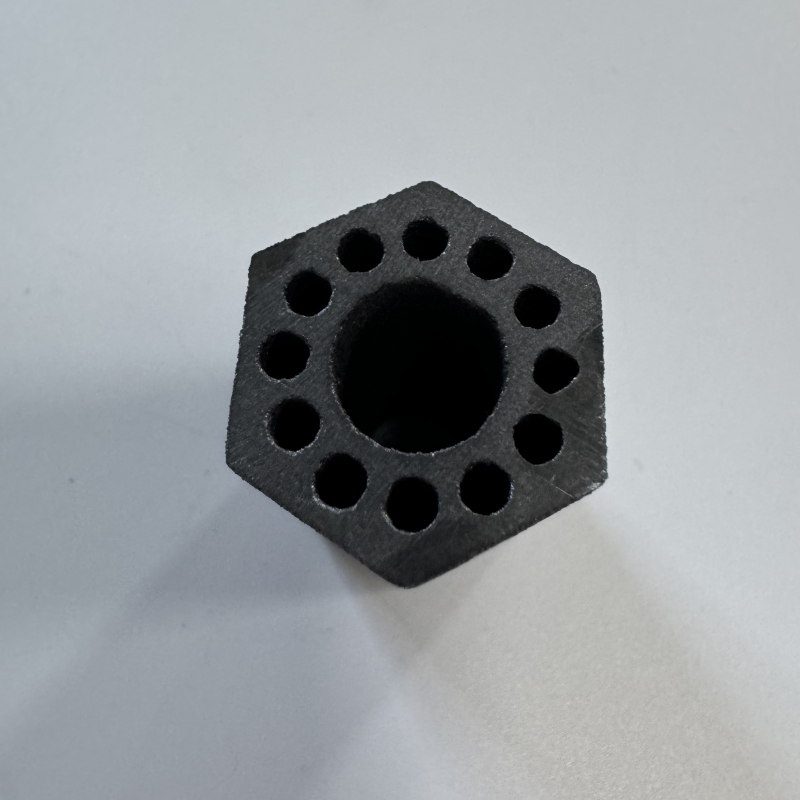
Product brief description:
Silicon carbide tubes inherit the excellent properties of silicon carbide ceramics, have outstanding high-temperature mechanical properties, can maintain high strength at a high temperature of about 1600℃, and also possess oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. They are widely used in industries such as petroleum, chemical engineering, metallurgy, and electric power. They can transport high-temperature, corrosive, or abrasive materials and can also be used as key components of high-temperature equipment.
Product details description:
Silicon carbide tubes take silicon carbide ceramics as the core base material and fully inherit a series of outstanding properties of silicon carbide materials. They not only have remarkable high strength and hardness, which are sufficient to resist impact and extrusion in high - load industrial scenarios, but also have extraordinary wear resistance. Even when subjected to continuous scouring by granular materials for a long time, they can maintain structural integrity. In terms of high - temperature resistance, silicon carbide tubes are particularly outstanding. Conventional products can operate stably in high - temperature environments above 1000°C, and some silicon carbide tubes prepared by special processes can even adapt to more extreme temperature conditions. At the same time, their excellent thermal shock resistance enables them not to crack or be easily damaged when the temperature changes sharply. In addition, silicon carbide tubes also have excellent corrosion resistance, which can effectively resist the erosion of many corrosive substances such as acids and alkalis. Coupled with high thermal conductivity and good oxidation resistance, they not only ensure thermal conduction efficiency but also can remain stable for a long time in high - temperature environments and are not easy to fail due to oxidation.
It is precisely by virtue of these outstanding properties that silicon carbide tubes have been widely used in high-temperature, high-wear, and strong-corrosion working conditions in many industrial fields. In the metallurgical industry, in equipment such as medium-frequency forging furnaces, various heat treatment electric furnaces, and metallurgical sintering furnaces, silicon carbide tubes are used to transport materials such as high-temperature metal particles and ore powder, stably meeting the operational requirements of high temperature and high wear. In the power industry, key parts such as ash conveying pipelines and coal powder pipelines in power plants also rely on silicon carbide tubes to resist the wear and scouring of hard particles such as coal ash, ensuring the continuous operation of power production. In the chemical industry, silicon carbide tubes can work reliably whether transporting corrosive and abrasive chemical raw materials or processing granular materials, even in harsh scenarios such as gas purification, heat exchange, and long-distance transportation of chemical media. Even in industries with strict requirements for precision and durability such as lithium battery production, silicon carbide wear-resistant straight tubes can also withstand high temperatures and strong pressures in the production process, greatly reducing the risk of wear and leakage. In addition, in the smelting of non-ferrous metals, the high-temperature transportation systems in the new energy and resource industries, and the manufacturing of core equipment components, silicon carbide tubes have also become an indispensable choice.
The advantages of silicon carbide tubes are very significant. Firstly, they have a long service life and low maintenance costs. Their high wear resistance fundamentally extends the service life of the pipelines, reduces the frequency of maintenance and replacement, and saves a large amount of costs for the long-term operation of enterprises. Secondly, they have super adaptability to high-temperature scenarios, breaking through the temperature limitations of ordinary pipes and allowing industries that rely on high-temperature processes such as metallurgy and power to have more stable pipeline solutions. Moreover, in strong corrosion environments, their corrosion resistance enables them to operate reliably for a long time, greatly expanding the application scenario boundaries of pipelines. Meanwhile, high strength and high hardness endow silicon carbide tubes with excellent impact resistance and compression resistance, which are sufficient to withstand the strong scouring of materials and the pressure during system operation. In addition, good thermal conductivity can significantly improve thermal management efficiency in scenarios that require heat dissipation or heat exchange, such as the heat conduction link of thermal equipment, further optimizing the industrial production process.
In terms of production and connection processes, silicon carbide tubes mostly adopt the high-temperature sintering process. After silicon carbide powder is made into a green body, it is fired at high temperature to achieve the densification of the material, thereby ensuring that core properties such as strength, wear resistance, and high-temperature resistance meet the standards. The connection methods are flexible and diverse; welding, hot press sealing welding, flange connection, etc. can all be selected according to actual working condition requirements, which ensures the reliability and sealing performance of pipeline connections and effectively prevents material leakage or heat loss.
It is worth mentioning that, relying on the characteristics of silicon carbide as a "third-generation wide-bandgap semiconductor material", such as high-pressure resistance and high-temperature stability, silicon carbide tubes can also play a unique role in some high-temperature and high-pressure power electronics-related equipment, such as protective tubes for high-temperature power components and protective tubes for thermal measurement. This further reflects its application potential in high-end industrial fields.
With the continuous advancement of industrial technology, the application scenarios of silicon carbide tubes are still continuously expanding, providing reliable pipeline support for more high-difficulty industrial operations.
Product Parameter Table
| Max temperature of Application |
℃ |
1600 |
1380 |
1650 |
| Density |
g/cm³ |
> 3.1 |
> 3.02 |
> 2.6 |
| Open Porosity |
% |
< 0.1 |
< 0.1 |
15% |
| Bending Strength |
Mpa |
> 400 |
250(20℃) |
90-100(20℃) |
|
Mpa |
|
280(1200℃) |
100-120 (1100℃) |
| Modulus of Elasticity |
Gpa |
420 |
330(20℃) |
240 |
|
Gpa |
|
300 (1200℃) |
|
| Thermal Conductivity |
W/m.k |
74 |
45(1200℃) |
24 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion |
K⁻¹×10⁻⁶ |
4.1 |
4.5 |
4.8 |
| Vickers Hardness HV |
Gpa |
22 |
20 |
|
| Acid Alkaline-proof |
|
excellent |
excellent |
excellent |




![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()