Production Process and Workflow of Quartz glass Tubes
Quartz tubes are primarily made from fused quartz (amorphous silicon dioxide). The most advanced and common industrial method for producing continuous lengths of quartz tubing is the Continuous Melting and Drawing Process.
The entire workflow can be divided into two main stages:
Stage 1: Continuous Melting & Tube Drawing (The Core Process)
This is the critical stage where raw materials are transformed into a continuous quartz tube.
- Materials: High-purity natural quartz sand or synthetic quartz granules (from a flame fusion process). The purity grade is selected based on the final application (e.g., optical, semiconductor).
- Processing: The raw materials undergo rigorous cleaning, acid leaching, and drying to remove metallic ions, dust, and moisture.
- Continuous Feeding & Melting
- The purified quartz material is fed continuously into a specialized vertical continuous melting furnace.
- The furnace chamber is typically made of refractory metals (e.g., molybdenum) or graphite and is maintained under a protective atmosphere (e.g., helium, nitrogen) to prevent oxidation and contamination.
- High temperatures (approximately 2000°C) are generated via graphite or tungsten electrodes, melting the feedstock in the upper part of the furnace to form a homogeneous, bubble-free quartz melt.
- The molten quartz flows downward to the bottom of the furnace and through a precision forming die or mandrel.
- This die determines the final outer diameter and wall thickness of the tube. It is typically a concentric high-temperature graphite mold.
- By precisely controlling the melt temperature, viscosity, drawing speed, and internal gas pressure, the softened quartz glass is "drawn" upward or downward into a continuous tube with stable dimensions.
- The newly formed quartz glass tube contains significant internal thermal stress due to uneven cooling, making it extremely fragile.
- The drawn tube immediately passes through an in-line annealing furnace (a lehr). This furnace provides a slow and precisely controlled cooling zone, allowing the tube to gradually cool through a critical temperature range (e.g., 1100°C to 800°C).
- Purpose: To permanently relieve internal stress, thereby stabilizing the mechanical properties of the quartz tube and preventing it from cracking during subsequent handling or use.
- Cutting & Preliminary Inspection
- The continuous tube is cut to standard lengths.
- A preliminary inspection is conducted for visible defects like bubbles, inclusions, scratches, and to check dimensional tolerances (OD and wall thickness).
Stage 2: Secondary Processing (Customization for End-Use)
The semi-finished tubes undergo various finishing processes tailored to customer specifications.
- Cutting: Quartz glass tube are cut to custom lengths using dedicated quartz cutters (e.g., diamond wheel saws or laser cutters) to ensure clean, square ends without chipping.
- Chamfering/Beveling: The cut ends are ground to a smooth, rounded finish to prevent stress concentration and ensure operator safety.
- A thorough cleaning process is employed using high-purity water, acid solutions (e.g., HF/HNO₃ mixture), and solvents to remove all contaminants introduced during cutting and handling.
- Heat Treatment (Fire Polishing)
- Purpose: For applications requiring high purity and smooth inner surfaces (e.g., semiconductor industry), the tube's ends or entire interior may undergo fire polishing.
- Method: The quartz glass tube surface is momentarily heated to its softening point using a hydrogen-oxygen torch or plasma arc. Surface tension causes the molten layer to become perfectly smooth and sealed, eliminating micro-cracks, reducing surface roughness, and driving off surface impurities.
- Result: Fire-polished quartz glass tube exhibit higher mechanical strength and increased resistance to devitrification.
- Thermal Bending: For custom shapes, a section of the quartz glass tube is locally heated until soft and then bent over a form or mold.
- End Sealing: The end(s) of the quartz glass tube are melted and closed using a high-temperature torch to create quartz ampoules, sleeves, or other closed containers.
Advantage of quartz glass tube
-
Quartz glass tube is corrosion resistance
In addition to hydrofluoric acid, quartz glass almost does not react with other acids for chemical treatment, and its acid resistance is 30 times that of its acid resistance ceramic and stainless steel 150 times.
- Excellent electrical insulation performance
The resistance value of quartz glass tube is equivalent to 10,000 times that of ordinary glass. It is an excellent electrical insulating material and maintains good electrical properties even at high temperatures
- High temperature resistance
The ability of quartz glass tubes to maintain their performance and structural stability in high temperature environments
Applications fields
Quartz glass tube is mainly used in electric light source, electrical (electrical), semiconductor, optical communication, military, metallurgy, building materials, chemical industry, machinery, electric power, environmental protection and other fields.
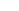
Technical Data of Opaque Quartz Tube